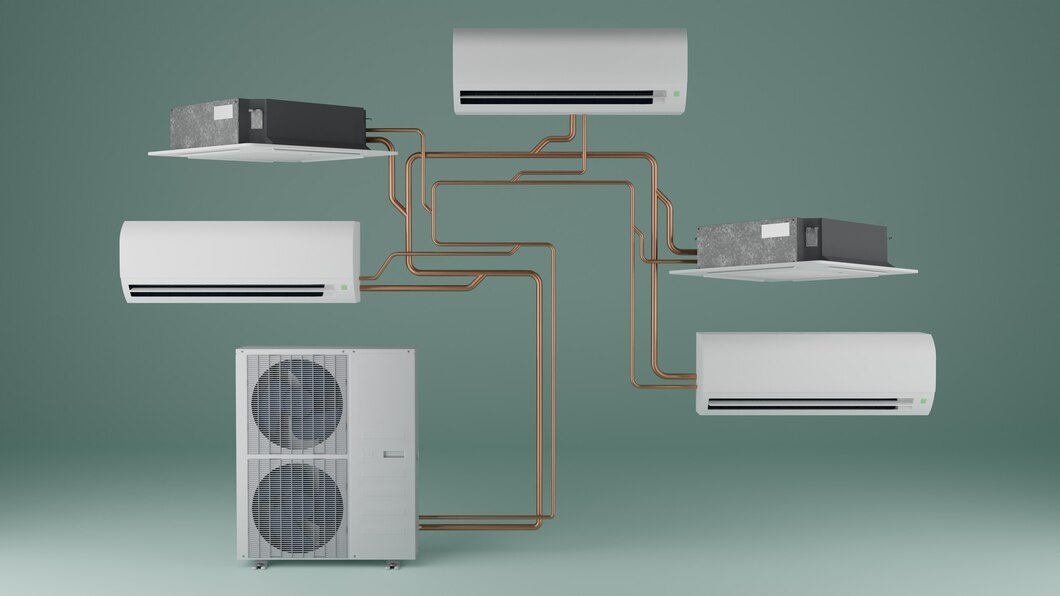
Building Automation Systems (BAS) are centralized networks of hardware and software that monitor and control a building’s electrical and mechanical systems. These systems include HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), lighting, security, and other essential components. By integrating these functions, BAS can optimize the energy efficiency, comfort, and safety of the building. Modern BAS use sensors and advanced algorithms to continuously collect data, allowing for real-time adjustments and predictive maintenance, thereby reducing operational costs and extending the lifespan of equipment.

The primary benefit of BAS is energy efficiency. By precisely controlling heating, cooling, lighting, and ventilation, BAS can significantly reduce energy consumption. For example, BAS can adjust the HVAC system based on occupancy patterns, ensuring that energy is not wasted on empty rooms. Similarly, lighting can be dimmed or turned off when natural light is sufficient or when spaces are unoccupied. These smart adjustments lead to substantial cost savings and contribute to sustainability goals by reducing the building’s carbon footprint.
Another crucial aspect of BAS is enhancing occupant comfort and safety. BAS can maintain optimal indoor air quality and temperature, creating a more pleasant environment for occupants. Security systems integrated into BAS can include access control, video surveillance, and alarm systems, ensuring a secure environment. In the event of an emergency, such as a fire, the BAS can automatically trigger alarms, control smoke ventilation, and guide occupants to safety through emergency lighting and signage.
Furthermore, BAS provide facility managers with valuable insights through data analytics. By analyzing trends and anomalies, managers can identify inefficiencies and potential issues before they become significant problems. Predictive maintenance, enabled by BAS, allows for timely servicing of equipment, preventing unexpected failures and downtime. This proactive approach not only enhances the reliability of building systems but also extends their operational lifespan.
In summary, Building Automation Systems represent a significant advancement in the management of modern buildings. They offer enhanced energy efficiency, improved comfort and safety, and valuable operational insights, making them an indispensable tool for facility managers and building owners. As technology continues to evolve, BAS are expected to become even more sophisticated, further revolutionizing the way buildings are managed and operated.
Enhancing Efficiency and Comfort with Building Automation Systems
In today’s world, the integration of technology into everyday life has become increasingly prevalent, and one of the most significant advancements in this regard is the development of Building Automation Systems (BAS). These systems have revolutionized the way buildings are managed, offering a range of benefits that enhance efficiency, comfort, and safety.

Key Benefits of Building Automation Systems (BAS)
- Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
- Precise control of HVAC, lighting, and ventilation systems.
- Adjustment based on real-time occupancy data.
- Reduced energy consumption and operational costs.
- Supports sustainability efforts and reduces carbon footprint.
- Enhanced Occupant Comfort
- Maintains optimal indoor air quality and temperature.
- Creates a pleasant and comfortable environment for occupants.
- Improved Safety and Security
- Integrated security features like access control and video surveillance.
- Automatic triggering of alarms and smoke ventilation during emergencies.
- Guiding occupants to safety with emergency lighting and signage.
- Data-Driven Insights
- Continuous collection and analysis of data.
- Identification of inefficiencies and potential issues.
- Valuable operational insights for facility managers.
- Predictive Maintenance
- Timely servicing of equipment based on data analysis.
- Prevention of unexpected failures and downtime.
- Extended operational lifespan of building systems.
- Future Technological Advancements
- Integration of artificial intelligence and IoT.
- Enhanced functionality and efficiency.
- Greater benefits for building owners and occupants.
- Operational Optimization
- Real-time adjustments to building systems.
- Minimization of waste and maximization of system performance.
- Sustainability Goals
- Contribution to environmental sustainability.
- Alignment with green building standards and certifications.
- Increased Property Value
- Modernized building management systems can increase the value of the property.
- Attractive feature for potential buyers and tenants.
- Regulatory Compliance
- Ensures compliance with energy and safety regulations.
- Helps avoid fines and legal issues related to non-compliance.
Future Trends in Building Automation Systems
- Artificial Intelligence Integration
- AI-driven analytics and control.
- Enhanced predictive maintenance and operational efficiency.
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Increased connectivity of building systems.
- Improved data collection and system integration.
- Sustainable Building Practices
- BAS as a cornerstone in achieving sustainability goals.
- Greater emphasis on eco-friendly building operations.
- Advanced User Interfaces
- More intuitive and user-friendly interfaces for building managers.
- Improved monitoring and control capabilities.
- Scalability and Flexibility
- Systems that can easily scale with the building’s needs.
- Flexible solutions that can adapt to various types of buildings.
By leveraging these benefits and keeping abreast of future trends, Building Automation Systems can significantly enhance the management and operation of modern buildings.
What are Building Automation Systems?
Building Automation Systems (BAS) are centralized networks of hardware and software designed to monitor and control a building’s various systems, such as HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), lighting, and security. These systems work together to optimize the performance of a building, ensuring that all components operate efficiently and harmoniously. For a deeper understanding of BAS, you can explore this detailed guide.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
One of the most compelling benefits of BAS is their ability to improve energy efficiency. By precisely controlling heating, cooling, lighting, and ventilation, BAS can significantly reduce energy consumption. For example, these systems can adjust the HVAC settings based on real-time occupancy data, ensuring that energy is not wasted in unoccupied spaces. This smart management of resources not only leads to substantial cost savings but also supports sustainability efforts. For more on how BAS contribute to energy efficiency, visit Energy.gov’s insights on energy management.
Enhancing Occupant Comfort and Safety
Beyond energy savings, BAS play a crucial role in enhancing occupant comfort and safety. These systems can maintain optimal indoor air quality and temperature, creating a more pleasant environment for building occupants. Additionally, integrated security features such as access control, video surveillance, and alarm systems ensure a safe and secure environment. In emergencies, BAS can automatically trigger alarms, manage smoke ventilation, and guide occupants to safety with emergency lighting and signage. Learn more about the safety benefits of BAS from Safe Buildings.
Data-Driven Insights and Predictive Maintenance
BAS also provide facility managers with valuable insights through data analytics. By continuously collecting and analyzing data, these systems can identify inefficiencies and potential issues before they become significant problems. This predictive maintenance capability allows for timely servicing of equipment, preventing unexpected failures and downtime. As a result, the operational lifespan of building systems is extended, and reliability is enhanced. For a comprehensive look at how data analytics is transforming building management, check out Analytics for Building Efficiency.

Future of Building Automation Systems
As technology continues to evolve, the capabilities of BAS are expected to grow even more sophisticated. Innovations in artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) are poised to further enhance the functionality and efficiency of these systems, making them an indispensable tool for facility managers and building owners. Stay updated with the latest trends in BAS by visiting Smart Building Trends.
In conclusion, Building Automation Systems represent a significant advancement in modern building management. Their ability to improve energy efficiency, enhance comfort and safety, and provide valuable operational insights makes them a crucial component in the management of contemporary buildings. As BAS technology continues to advance, its impact on the built environment is set to increase, promising even greater benefits for building owners and occupants alike.
The Future of Building Automation Systems (BAS)
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Enhanced Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms will predict equipment failures before they occur, allowing for proactive maintenance.
- Optimized Energy Management: AI-driven analytics will fine-tune energy consumption, leading to further reductions in costs and carbon footprint.
- Adaptive Learning: Systems will learn from building usage patterns and continuously improve their efficiency.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Expansion
The expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing Building Automation Systems (BAS) by enhancing connectivity and data integration across various building components. With more devices and sensors becoming interconnected, IoT enables a more comprehensive and real-time view of building operations. This increased connectivity facilitates seamless communication between different systems, such as HVAC, lighting, and security, leading to more efficient and synchronized management. Real-time monitoring capabilities allow for immediate detection and response to operational issues, improving overall system reliability and performance. Furthermore, IoT’s interoperability ensures that components from different manufacturers can work together seamlessly, fostering greater flexibility and scalability in building management. As IoT technology advances, the ability to collect and analyze vast amounts of data will drive more informed decision-making, optimize resource use, and enhance the overall efficiency of building operations.
- Increased Connectivity: More devices and sensors will be connected, providing richer data for analysis and control.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Enhanced real-time monitoring of building systems will lead to more immediate responses to any issues.
- Interoperability: Seamless integration of various building systems, regardless of manufacturer, enhancing overall system efficiency.
- Sustainable and Green Building Practices
- Net-Zero Energy Buildings: BAS will be crucial in achieving net-zero energy goals by optimizing energy use and integrating renewable energy sources.
- Eco-Friendly Materials and Systems: Increased focus on sustainability will lead to the use of more eco-friendly building materials and systems.
- Regulatory Compliance: Future BAS will help buildings comply with stricter environmental regulations and certifications.
- Advanced Data Analytics
- Big Data Utilization: Leveraging big data to gain deeper insights into building performance and occupant behavior.
- Machine Learning: Applying machine learning to detect patterns and anomalies, improving system reliability and efficiency.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Data-driven decision-making processes will enhance the management of building operations.
- Human-Centric Building Automation
- Improved Occupant Experience: BAS will focus on enhancing the comfort, health, and productivity of building occupants.
- Personalized Environments: Systems will adjust lighting, temperature, and other parameters based on individual preferences and needs.
- Wellness and Health Integration: Monitoring and maintaining indoor air quality, humidity levels, and other factors to promote occupant health.
- Cybersecurity Enhancements
- Robust Security Protocols: Future BAS will incorporate advanced cybersecurity measures to protect against hacking and data breaches.
- Regular Updates and Patches: Continuous updates and security patches to address vulnerabilities.
- Data Privacy: Ensuring the privacy and security of data collected by building automation systems.
- Sca
Scalability and flexibility are pivotal aspects of modern Building Automation Systems (BAS), enabling them to adapt to evolving needs and technological advancements. Scalable BAS are designed to grow alongside a building’s expansion, allowing for the integration of additional components and systems without significant overhauls. This modular approach ensures that as new technologies emerge or building requirements change, the system can be easily upgraded or expanded. Flexibility is equally important, as it allows BAS to be customized to fit diverse building types and operational needs. Whether adapting to different layouts, user preferences, or functional requirements, flexible BAS can be tailored to provide optimal performance. The combination of scalability and flexibility not only enhances the long-term value of building automation investments but also ensures that systems remain effective and relevant in the face of future changes and advancements.
- Modular Systems: Easily upgradable and scalable systems to accommodate building expansions and technological advancements.
- Flexible Solutions: Customizable solutions that can adapt to different types of buildings and user requirements.
- Cloud-Based Platforms: Increased use of cloud-based solutions for remote monitoring and control.
- Integration with Smart Cities
- Smart Grid Interaction: BAS will interact with smart grids for optimized energy distribution and consumption.
- Urban Efficiency: Contribution to the efficiency and sustainability of urban environments through integrated smart city initiatives.
- Community-Wide Benefits: Enhanced collaboration between buildings, leading to community-wide energy and resource savings.
- User-Friendly Interfaces
- Intuitive Control Panels: More user-friendly and intuitive interfaces for building managers and occupants.
- Mobile Accessibility: Enhanced mobile apps for remote monitoring and control of building systems.
- Voice and Gesture Control: Integration of voice and gesture control for more seamless interaction with building systems.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
- Maintenance and Training: Use of AR and VR for training maintenance staff and visualizing building systems.
- Remote Assistance: Technicians can use AR for remote assistance and troubleshooting.
- Enhanced Visualization: VR for better visualization of building designs and system layouts.
The future of Building Automation Systems is poised to be transformative, driven by technological advancements and a growing emphasis on sustainability, efficiency, and occupant well-being. As BAS continue to evolve, they will play an increasingly vital role in the management and operation of smart, sustainable buildings and cities.